The Incredible Pineal Gland and Its Massive Role on the Effects of Cannabis
For all of you avid cannabis consumers out there, have you noticed that if you smoke weed during the day versus the night time or when the sun is setting, that the affects of cannabis are different? If someone consumes cannabis very regularly, they may have trouble telling the difference. But, consistent cannabis consumers may have noticed a difference and if not, maybe they will after learning about the pineal gland’s role in the psychoactive affects of cannabis.
 By this point in time you may have heard that mammals and many other animals have an endocannabinoid system. This internal system links up with the phytocannabinoids our bodies produce on their own and with the cannabinoids found from external sources like the Cannabis sativa plant. We also have other internal systems like our opioid system which connects with harder drugs like heroin and many prescription drugs. Within our brain, especially the more critical parts, the opioid system is prevalent which is what makes opioids so dangerous. The endocannabinoid system is more a of a peripheral system, but deep within the center of the brain is the pineal gland and it has a functioning endcocannabinoid system.
By this point in time you may have heard that mammals and many other animals have an endocannabinoid system. This internal system links up with the phytocannabinoids our bodies produce on their own and with the cannabinoids found from external sources like the Cannabis sativa plant. We also have other internal systems like our opioid system which connects with harder drugs like heroin and many prescription drugs. Within our brain, especially the more critical parts, the opioid system is prevalent which is what makes opioids so dangerous. The endocannabinoid system is more a of a peripheral system, but deep within the center of the brain is the pineal gland and it has a functioning endcocannabinoid system.
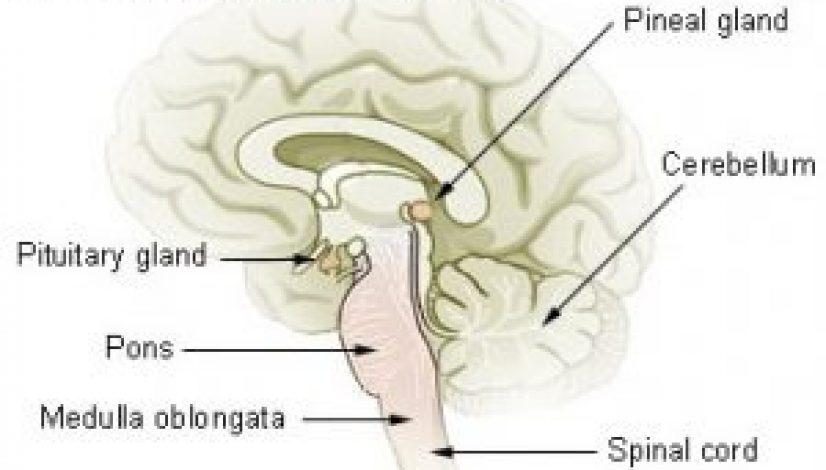
 The Pineal gland is still a mystery in many ways to scientists. It is part of our endocrine system and is only about a 1/3 of an inch long and is shaped somewhat like a pine cone which is where it gets its name from. People have often referred to it as our third eye and the famous French scientist René Descartes believed it was the heart of our soul. The Pineal gland is light sensitive and in some animals like the tuatara lizard found in New Zealand, the gland even has a lens, retina and cornea like an actual eye. The pineal gland is responsible for the incredibly important hormone melatonin which induces sleep and is an important factor in our moods. When light shines on the pineal gland it produces less melatonin, when it is dark it produces more melatonin to make us go to sleep. You could look at it as our natural internal 24 hour clock.
The Pineal gland is still a mystery in many ways to scientists. It is part of our endocrine system and is only about a 1/3 of an inch long and is shaped somewhat like a pine cone which is where it gets its name from. People have often referred to it as our third eye and the famous French scientist René Descartes believed it was the heart of our soul. The Pineal gland is light sensitive and in some animals like the tuatara lizard found in New Zealand, the gland even has a lens, retina and cornea like an actual eye. The pineal gland is responsible for the incredibly important hormone melatonin which induces sleep and is an important factor in our moods. When light shines on the pineal gland it produces less melatonin, when it is dark it produces more melatonin to make us go to sleep. You could look at it as our natural internal 24 hour clock.
Where does consuming cannabis come into play? Well, lots of blood flows through the pineal gland because unlike other glands in the brain it is not obstructed by the blood-brain membrane. When we consume cannabis, the THC makes its unobstructed way to the pineal gland attaching to the CB receptors in the gland slowing the production of melatonin. In the middle of the day when there is lots of light, the pineal gland is not producing as much melatonin anyways. But, as the sun begins to go down active cannabinoids along with THC are mixing with melatonin altering our state of perception.
 Melatonin
Melatonin
If cannabis ends up being a sleep inhibitor, then why do people get sleepy when they smoke or consume marijuana in some way? There are a couple of things to consider, scientists have done most of their research on rats, not people, since researching cannabis is challenging due to the Schedule 1 status. So, people may be a bit different then rats, but then again people are different from other people. Maybe it is the difference between consuming an indica dominant strain or a sativa dominant strain. Perhaps it is a person’s tolerance level for cannabis. Mood disorders are common in people as well so a lot of it will have to do with the hormones that a person naturally produces. Here is what understanding the pineal gland provides us the knowledge of; cananbis consumption affects everyone a little differently and the time of day you consume cannabis affects the high as well.
Tags
cannabisCB receptorsendocannabinoid systemMarijuana Newsmarijuana researchmelatoninphytocannabinoidspineal glandsleepTHC